Simulation Based Inference#
In this example we will go through an example setting up Nested Sampling as an external sampler for the sbi package. This uses the ability to integrate torch with blackjax, as detailed more in PyTorch language integration
Neural Likelihood Estimation with Nested Sampling#
This example demonstrates how to use BlackJAX nested sampling as a posterior sampler for simulation-based inference (SBI) with neural likelihood estimation (NLE).
Prerequisites#
Install the required packages:
pip install git+https://github.com/handley-lab/blackjax
pip install sbi torch anesthetic numpy tqdm
NSPosterior Implementation#
First, we define a custom posterior class that uses BlackJAX nested sampling to sample from the posterior distribution given a trained likelihood estimator and prior.
from typing import Optional
import torch
import numpy as np
import jax
import jax.numpy as jnp
import blackjax
from blackjax.ns.utils import finalise
import anesthetic
import tqdm
from sbi.inference.posteriors.base_posterior import NeuralPosterior
from sbi.inference.potentials.likelihood_based_potential import LikelihoodBasedPotential
class NSPosterior(NeuralPosterior):
"""Nested Sampling posterior for sbi.
Uses BlackJAX nested sampling to sample from posterior distributions
when given a likelihood estimator and prior.
Args:
likelihood: Trained likelihood estimator from NLE
prior: Prior distribution
num_live: Number of live points for nested sampling
num_inner_steps: Number of slice sampling steps
x_o: Observed data (can be set later with set_default_x)
num_delete: Number of points to delete per iteration (default: 1)
"""
def __init__(
self,
likelihood,
prior,
num_live,
num_inner_steps,
x_o=None,
num_delete=1,
):
self.num_live = num_live
self.num_delete = num_delete
self.num_inner_steps = num_inner_steps
potential_fn = LikelihoodBasedPotential(likelihood, prior, x_o)
super().__init__(potential_fn)
def _loglikelihood_fn(self, theta):
x_o_batch = self.default_x.unsqueeze(0).expand(1, theta.shape[0], -1)
return self.potential_fn.likelihood_estimator.log_prob(x_o_batch, condition=theta).squeeze(0)
def _logprior_fn(self, theta):
return self.potential_fn.prior.log_prob(theta)
def nested_samples(self) -> anesthetic.NestedSamples:
"""Run BlackJAX nested sampling and return anesthetic NestedSamples object.
Returns:
NestedSamples object containing particles, log-likelihoods, and birth
log-likelihoods that can be used for evidence calculation and diagnostics.
"""
def wrap_fn(fn, vmap_method='legacy_vectorized'):
def numpy_wrapper(theta):
x = torch.from_numpy(np.asarray(theta).copy()).float()
result = fn(x)
return result.detach().numpy()
def jax_wrapper(x):
out_shape = jax.ShapeDtypeStruct(x.shape[:-1], x.dtype)
return jax.pure_callback(numpy_wrapper, out_shape, x, vmap_method=vmap_method)
return jax_wrapper
algo = blackjax.nss(
logprior_fn=wrap_fn(self._logprior_fn),
loglikelihood_fn=wrap_fn(self._loglikelihood_fn),
num_delete=self.num_delete,
num_inner_steps=self.num_inner_steps,
)
prior_samples = self.potential_fn.prior.sample((self.num_live,))
initial_live = jnp.array(prior_samples.numpy())
rng_key = jax.random.PRNGKey(42)
live = algo.init(initial_live)
step = jax.jit(algo.step)
dead_points = []
with tqdm.tqdm(desc="Dead points", unit=" dead points") as pbar:
while (not live.logZ_live - live.logZ < -3):
rng_key, subkey = jax.random.split(rng_key)
live, dead = step(subkey, live)
dead_points.append(dead)
pbar.update(len(dead.particles))
ns_run = finalise(live, dead_points)
return anesthetic.NestedSamples(
data=ns_run.particles,
logL=ns_run.loglikelihood,
logL_birth=ns_run.loglikelihood_birth,
)
def sample(
self,
sample_shape: torch.Size = torch.Size(),
x: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
**kwargs
) -> torch.Tensor:
r"""Return samples from posterior distribution $p(\theta|x)$ with nested sampling.
Check the `__init__()` method for a description of all arguments as well as
their default values.
Args:
sample_shape: Desired shape of samples that are drawn from posterior. If
sample_shape is multidimensional we simply draw `sample_shape.numel()`
samples and then reshape into the desired shape.
Returns:
Samples from posterior with shape `(*sample_shape, theta_dim)`.
"""
self.potential_fn.set_x(self._x_else_default_x(x))
ns = self.nested_samples()
samples = ns.sample(torch.Size(sample_shape).numel())
samples_array = samples.drop(columns=['logL', 'logL_birth', 'nlive']).values
return torch.from_numpy(samples_array).reshape((*sample_shape, -1))
def sample_batched(self, sample_shape, x, **kwargs):
raise NotImplementedError("Batched sampling not available for nested sampling.")
/Users/yallup/projects/nested-sampling-book/.venv/lib/python3.11/site-packages/tqdm/auto.py:21: TqdmWarning: IProgress not found. Please update jupyter and ipywidgets. See https://ipywidgets.readthedocs.io/en/stable/user_install.html
from .autonotebook import tqdm as notebook_tqdm
Example: Sequential Neural Likelihood Estimation (SNLE)#
Now let’s use the NSPosterior class with neural likelihood estimation from the sbi package. This example demonstrates sequential neural likelihood estimation (SNLE), where the likelihood estimator is trained over multiple rounds using nested sampling to generate proposal samples for each round.
from sbi.inference import NLE
from sbi.utils import BoxUniform
num_dims = 2
num_sims = 1000
num_rounds = 2
prior = BoxUniform(low=torch.zeros(num_dims), high=torch.ones(num_dims))
simulator = lambda theta: theta + torch.randn_like(theta) * 0.1
x_o = torch.tensor([0.5, 0.5])
inference = NLE(prior)
proposal = prior
round_samples = []
for _ in range(num_rounds):
theta = proposal.sample((num_sims,))
x = simulator(theta)
likelihood = inference.append_simulations(theta, x).train()
posterior = NSPosterior(
likelihood, prior, num_live=500, num_inner_steps=20, num_delete=250
)
proposal = posterior.set_default_x(x_o)
round_samples.append(theta)
Neural network successfully converged after 118 epochs.
Dead points: 2500 dead points [00:05, 434.83 dead points/s]
Neural network successfully converged after 73 epochs.
Analyze Results with Anesthetic#
Get the nested samples as an anesthetic NestedSamples object for analysis and visualization.
nested_samples = posterior.nested_samples()
nested_samples.to_csv("nested_samples.csv")
print(f"Evidence: {nested_samples.logZ(100).mean() :.2f} ± {nested_samples.logZ(100).std() :.2f}")
Dead points: 2250 dead points [00:05, 436.69 dead points/s]
Evidence: -0.19 ± 0.07
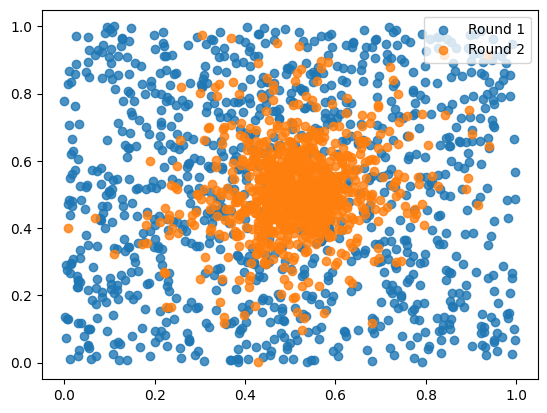
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
for i,ts in enumerate(round_samples):
plt.scatter(ts[:, 0], ts[:, 1], alpha=0.8, label=f"Round {i+1}")
plt.legend()
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x3306b08d0>
Visualize with Anesthetic#
The nested samples can be visualized using anesthetic’s plotting capabilities. You can either:
Use anesthetic from the command line:
anesthetic nested_samples.csv
Or plot directly in Python:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Create corner plot
fig = nested_samples.plot_2d([0, 1])
plt.show()
# Plot the log-evidence progression
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(nested_samples.logZ())
ax.set_xlabel('Iteration')
ax.set_ylabel('log(Z)')
plt.show()
